Microsegmentation Deployment Models

The Three Basic Microsegmentation Zero Trust Deployment Models
Microsegmentation is a powerful strategy for reducing the cyber-risk associated with critical assets and resources. For an introduction to microsegmentation, see our resource page, Microsegmentation, Explained.
Generally speaking, there are three major types of microsegmentation, each corresponding to one of the possible security insertion points:
- Agent-based, which inserts security at the OS level to protect applications
- Hypervisor-based, which inserts security at the hypervisor level and protects VMs
- Agentless, which inserts security outside the machine, at the network level
Of these, Zentera supports agent-based and agentless models. The three options are illustrated in the diagram below.
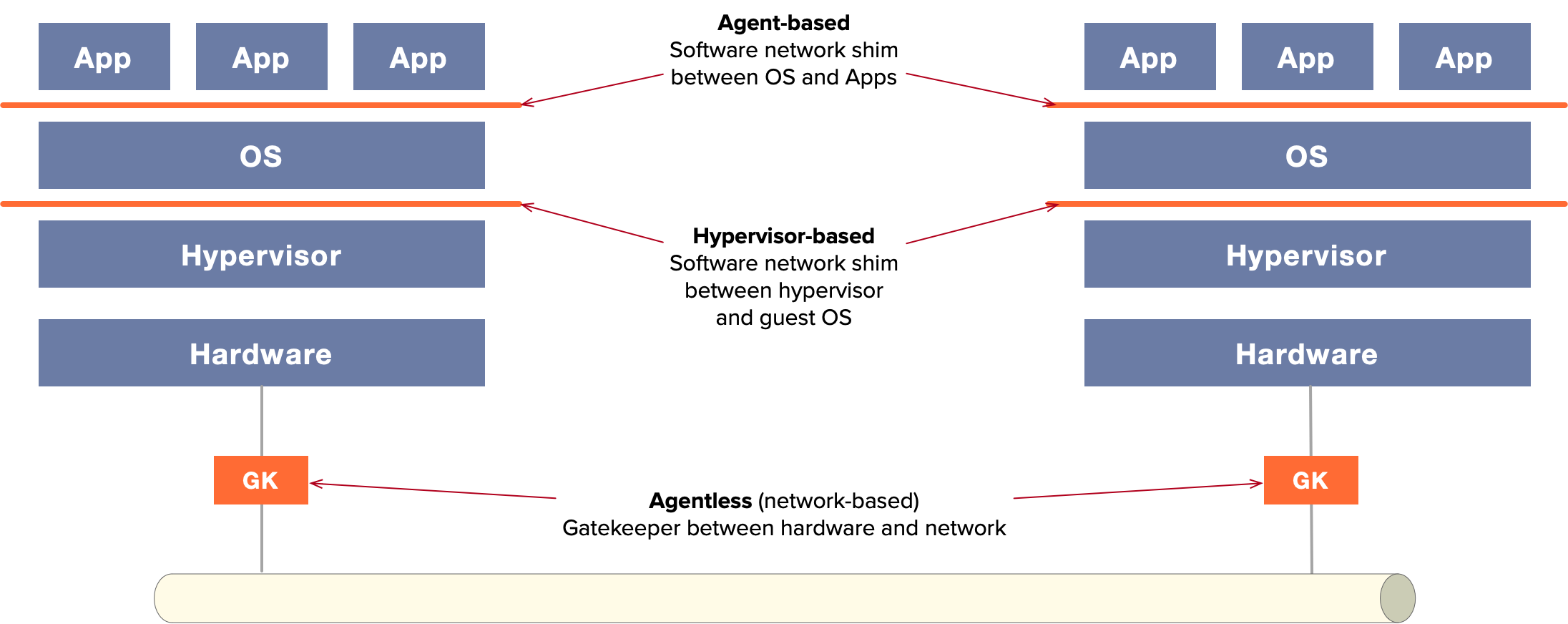
The Three Basic Types of Microsegmentation
Comparing Microsegmentation Zero Trust Methods
Each deployment method has its own strengths; while agent-based deployment works well for many application scenarios, other scenarios may call for an agentless approach. The table below compares the different models, outlining their applicability.
| Application | Agent | Hypervisor | Agentless | Notes |
| Bare Metal | ✓ | - | ✓ | |
| VMs | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Cloud | ✓ | - | ✓ | |
| Container | ✓ | - | ✓ | Agent model supports sidecar; agentless model protects only at the pod level |
| IoT | Varies | - | ✓ | |
| Supported by CoIPⓇ Access Platform | ✓ | - | ✓ |
Of these, the agent is the most versatile model; because it is closest to the workload it also has more detailed information and can implement a richer set of security features. The agent-based model is completely independent of infrastructure, and can be deployed across a wide range of cloud and datacenter infrastructure stacks without coupling to them.
The next is the agentless "gatekeeper"-based approach. The gatekeeper approach deploys an appliance (typically physical) inline with the workload being protected, and is recommended for workloads where the agent cannot be used – for example, OT environments. As agentless microsegmentation is deployed outside of the VM or server, it can work with any type of workload; deployment can be as simple as plugging and unplugging Ethernet cables to insert threat detection and filtering in front of a critical workload, such as a database server, an application server, machines on a factory floor, or critical infrastructure.
Take control of your network security with Microsegmentation Gatekeeper!
The most limited approach is hypervisor-based microsegmentation, because it is highly dependent on the hypervisor. A solution designed for a VMware datacenter cannot be ported to AWS, as customers have no access to the AWS hypervisor; similarly, hypervisor approaches cannot work for bare metal servers or IoT devices. For this reason, hypervisor-based microsegmentation is a relatively less popular approach for industry.
Selecting a Microsegmentation Method
Zentera recommends that any application that can support an agent should use it; once installed, administrators have full control over the microsegmentation settings of the server, and can begin to apply microsegmentation zero trust policies to lock down the attack surface.
For services that are too critical to allow agent installation, Zentera offers the gatekeeper approach. This allows administrators to rapidly insert security functions transparently, without touching critical servers. For more detail on Zentera's gatekeeper models, review the product page for our Microsegmentation Gatekeeper.